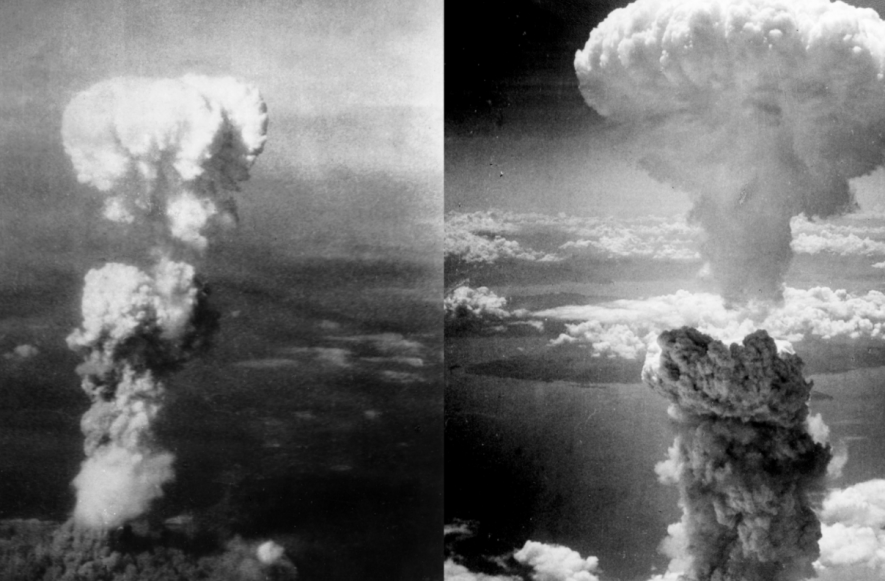
Tokyo: Hiroshima on Friday marked the 76th anniversary of the world’s first atomic bombing, as the mayor of the Japanese city urged global leaders to unite to eliminate nuclear weapons, just as they are united against the coronavirus.
Mayor Kazumi Matsui urged world leaders to commit to nuclear disarmament as seriously as they tackle a pandemic that the international community recognizes as “threat to humanity.”
“Nuclear weapons, developed to win wars, are a threat of total annihilation that we can certainly end, if all nations work together,” Matsui said. “No sustainable society is possible with these weapons continually poised for indiscriminate slaughter.”
The United States dropped the world’s first atomic bomb on Hiroshima on August 6, 1945, destroying the city and killing 140,000 people. It dropped a second bomb three days later on Nagasaki, killing another 70,000. Japan surrendered August 15, ending World War II and its nearly half-century of aggression in Asia.
But countries stockpiled nuclear weapons in the Cold War and a standoff continues to this day.
The global Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons took effect in January after years of civil effort joined by the atomic bombing survivors, or hibakusha. But while more than 50 countries have ratified it, the treaty notably lacks the US and other nuclear powers as well as Japan, which has relied on the US nuclear umbrella for its defense since the war’s end.
Matsui renewed his demand that his own government “immediately” sign and ratify the treaty and join the discussion, to live up to the long-cherished wish of atomic bombing survivors. He also demanded Japan provide productive mediation between nuclear and non-nuclear weapons states.
Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga, who attended the ceremony in Hiroshima, did not mention the treaty and instead stressed the need for a more “realistic” approach to bridge the nuclear and non-nuclear weapons states and by strengthening the NPT. Later at a news conference, Suga said he had no plan to sign the treaty.
“The treaty lacks support not only from the nuclear weapons states including the United States but also from many countries that do not possess nuclear arms,” Suga said. “What’s appropriate is to seek a passage to realistically promote the nuclear disarmament.”
Suga also apologised for inadvertently skipping parts of his speech including a pledge to pursue efforts toward achieving a nuclear-free world as head of the world’s only country to have suffered atomic attacks and fully aware of its inhumanity.
Many survivors of the bombings have lasting injuries and illnesses linked to the bombs and radiation exposure and faced discrimination in Japanese society.
The government began to medically support certified survivors in 1968 after more than 20 years of effort by the survivors.
As of March, 127, 755 survivors, whose average age is now almost 84, are certified as hibakusha and eligible for government medical support, according to the health and welfare ministry.
Suga announced last month the medical benefits would be extended to 84 Hiroshima survivors who had been denied aid because they were outside a government-set boundary. The victims were exposed to radioactive “black rain” that fell in the city after the bombing and fought a long legal battle for their health problems to be recognized.
Matsui urged Suga’s government to further widen support and have generous assistance quickly reach all those still suffering physical and emotional effects of radiation, including the black rain survivors who were not part of the lawsuit.
Thursday’s ceremony at the Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park was significantly scaled down because of the coronavirus pandemic and was also eclipsed by the Olympics being held in Tokyo, where even national NHK television quickly switched to the games after the main speeches.